Sky is blue..?
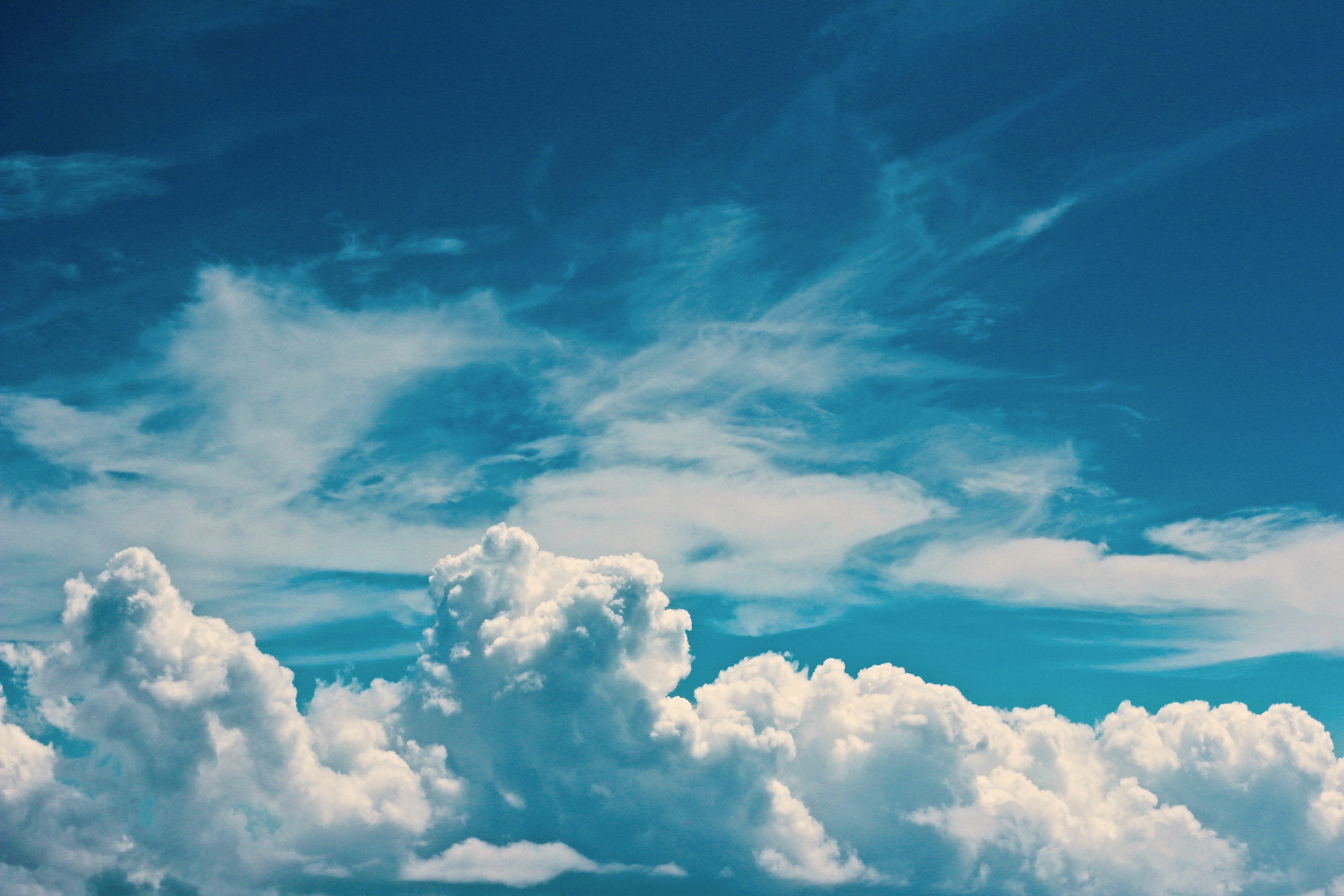

“The sun is up, the sky is blue”.. but why?
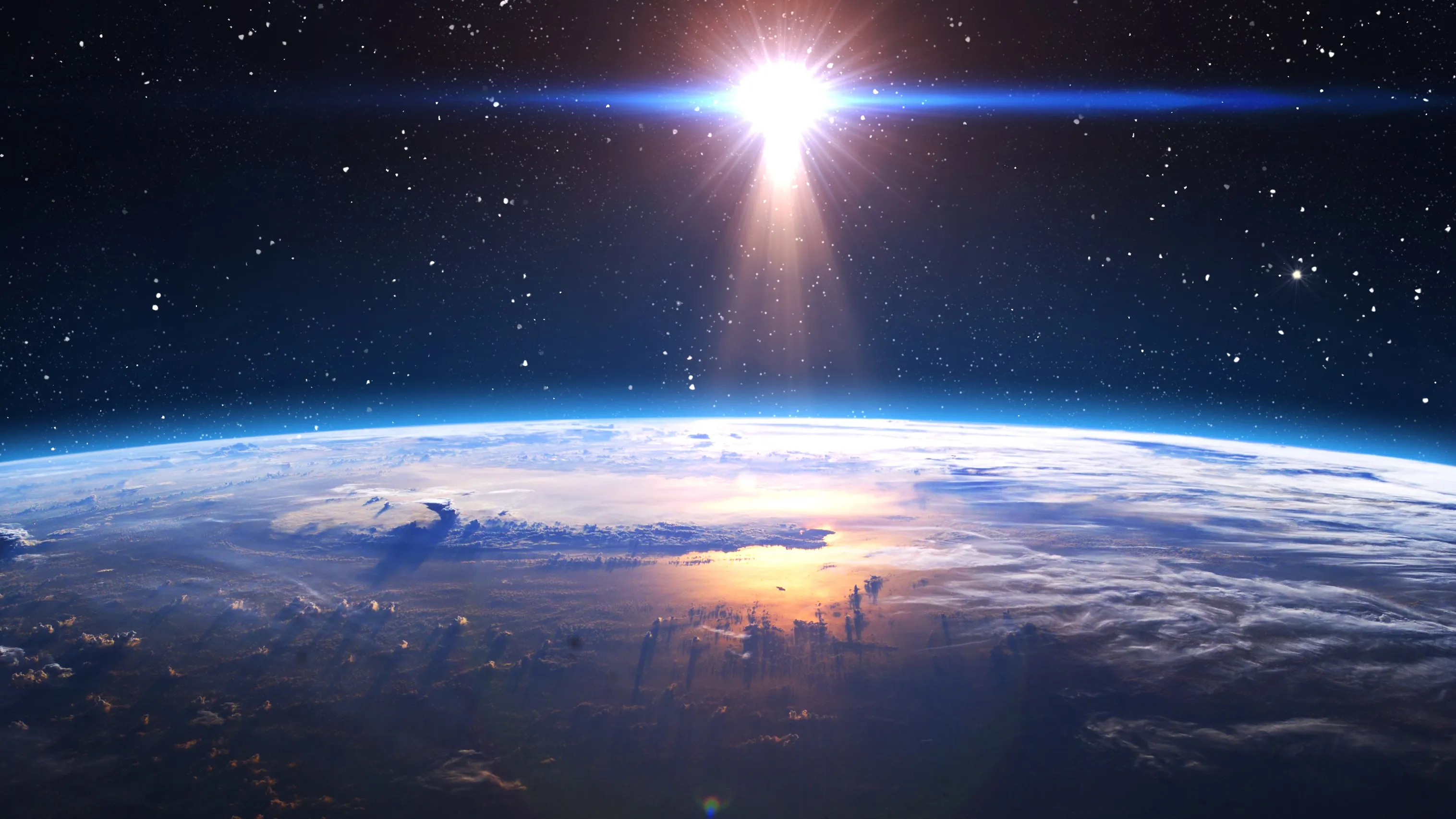
Have you ever wondered why when the sun is high up, the sky is so blue and so bright? In contrast, the outer space beyond us always looks like a black void?
Thanks to that one thing the earth has but the outer space is lack of: atmosphere. The earth’s atmosphere is made up of dust and air particles. Light from sun scatters and reflects when it hits these particles, eventually reaching our eyes. On the other hand, the outer space is “empty”, it has no atmosphere, light from the sun and other stars cannot be reflected and scattered off. That’s why even when the sun is shining, it’s still dark out there.
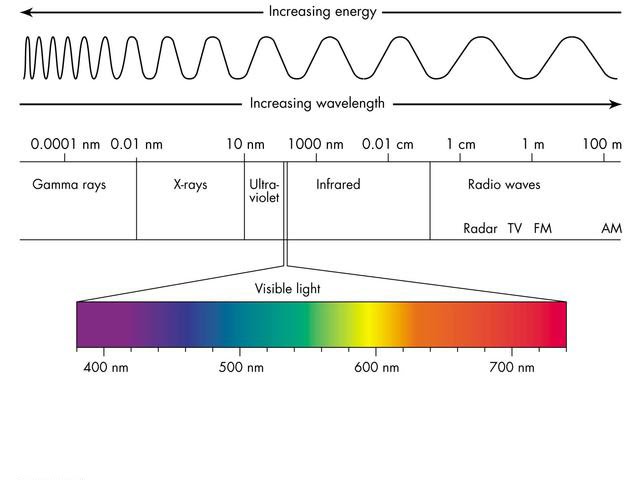
The 2nd question is, why the sky appears blue? It all has to do with how we perceive light. You see, the visible ‘white light’ we see is composed of 7 distinct colors (the rainbow color). Light is like an energy wave (at least in classic wave theory), its wavelength falls within a specific range of the electromagnetic radiation, with red having the shortest wavelength, and violet having the longest.
When the light reaches the earth’s atmosphere, much of the red, yellow and green wavelengths pass straight through the atmosphere. The blue and violet waves have just the right size to scatter off in every direction. As our eyes are not as sensitive to violet as they are to blue, hence the blue sky! 🏞🌏
Keywords
-
Atmosphere: A layer of gas or layers of gases that envelope a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low。
-
Classical Wave Theory: The intensity of the light determines the amplitude of the wave, and so a greater light intensity should cause the electrons on the metal to oscillate more violently and to be ejected with a greater kinetic energy.
-
Wavelength: Wavelength is the distance between identical points (adjacent crests) in the adjacent cycles of a waveform signal propagated in space or along a wire. Wavelength is inversely related to frequency, which refers to the number of wave cycles per second. The higher the frequency of the signal, the shorter the wavelength.
-
Electromagnetic Radiation: Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a form of energy that is all around us and takes many forms, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared-radiation, ultraviolet-radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. Sunlight is also a form of EM energy, but visible light is only a small portion of the EM spectrum, which contains a broad range of electromagnetic wavelengths.
Images

References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atmosphere
https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/wavelength
http://vergil.chemistry.gatech.edu/notes/quantrev/node4.html
https://www.livescience.com/38169-electromagnetism.html
https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/blue-sky/en/