Neonatal Jaundice
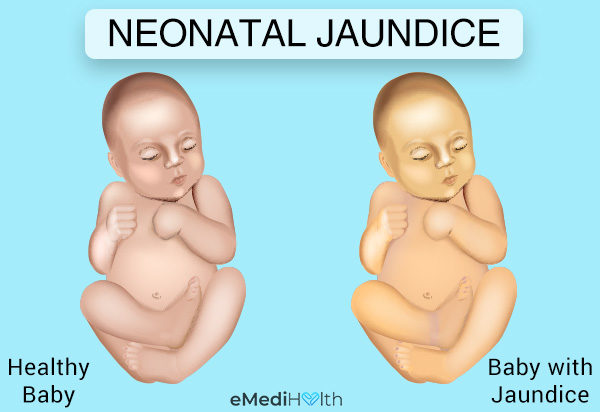
The skin and whites of the eyes start turning yellow…
Have you ever wondered how and why newborn babies develop jaundice that causes the skin and the whites of the eyes to turn yellow? Is treatment needed and what are the treatments?
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to anonymous for creating this series on Neonatal Jaundice.
Part1: Intoduction and Etiology
Have you ever wondered why most infants develop transient jaundice? What are the reasons and the treatments?
It is benign and self-limiting due to elevation of unconjugated (fat-liking) bilirubin (a yellow substance in blood) concentration during the first week of the newborn. This is called physiological jaundice/neonatal jaundice. Physiological jaundice occurs 24-36hours after birth and can last about 7-10days for term(37-42weeks) and 2 weeks for preterm(<37weeks) infants.
Neonatal jaundice is characterized by yellowish discoloration of the skin, conjunctiva and the sclera from elevated serum or plasma bilirubin in the newborn.
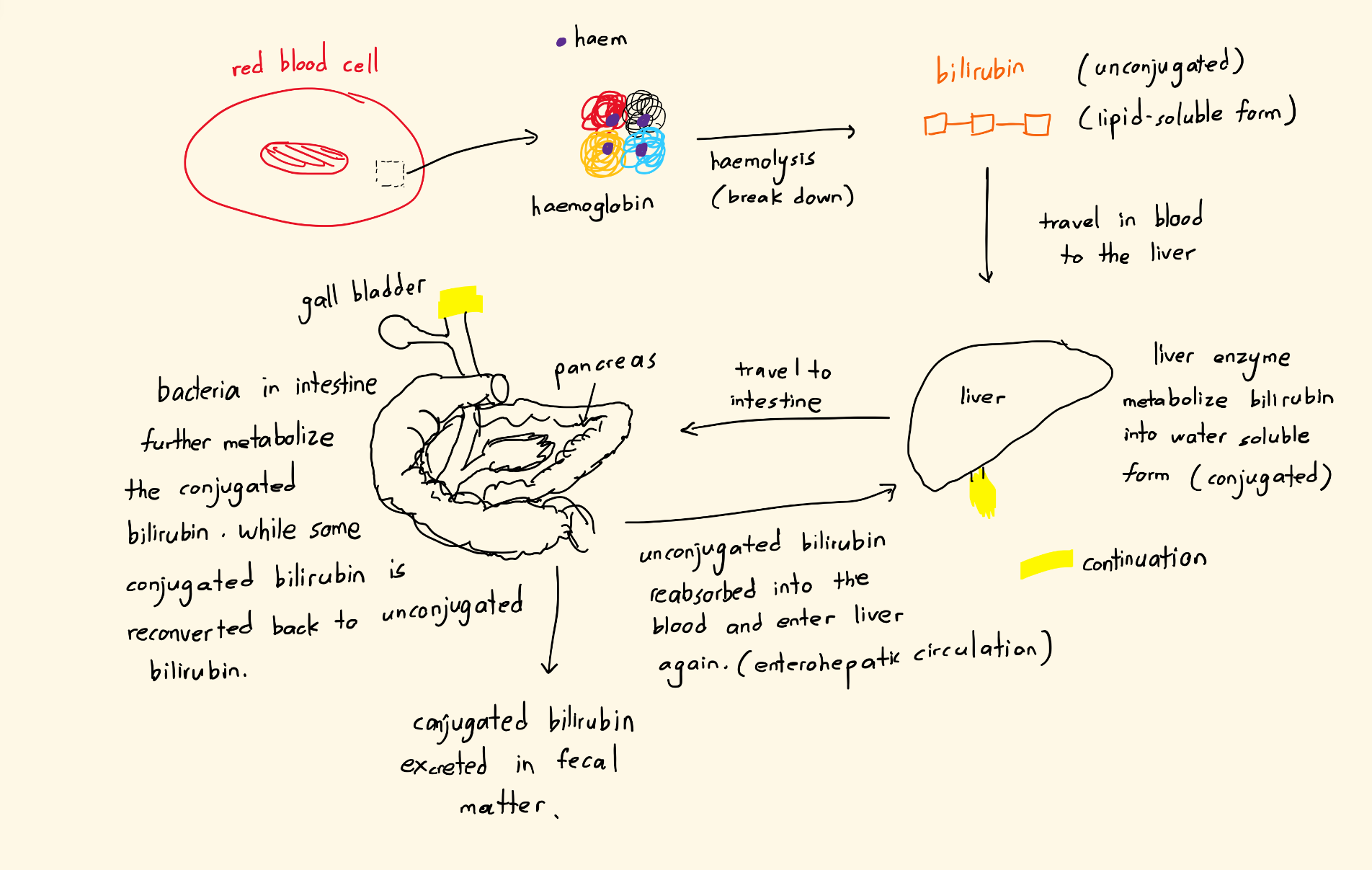
Etiology: Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (excessive fat-soluble bilirubin presence in blood) occurs because of increased production of bilirubin and a decreased in bilirubin clearance. There are 3 main mechanisms in newborns that contribute to physiological jaundice. (Discussed in next part)
Liver does the job of converting these fat-soluble bilirubin to be water-soluble(conjugation), and intestinal bacteria further metabolize them to be water soluble so that they can be excreted. Tho some of the bacteria reconvert back them into unconjugated form, and are then reabsorbed into the bloodstream and liver, thus increasing the bilirubin pool.
Images
Part 2: Etiology and treatment
In part 1 we discussed about the basic etiology of neonatal jaundice. Let’s look deep into that and discuss why newborns can easily develop it (3 main mechanism) and what are the treatments.
-
The life span of fetal erythrocytes(red blood cell) is short (
60to90days as compared to adultRBClifespan of120days), rendering the high rate of metabolism of fetal haemoglobin, increasing overall bilirubin concentration in blood. -
After birth, liver enzyme such as glucuronosyltransferase acts to conjugate the resulting bilirubin for excretion. However the enzyme is downregulated because before childbirth, the bilirubin have to stay in unconjugated form to pass through the placenta to be excreted by the mother.
-
Infant’s intestinal activity is low because excretion can be done through the placenta while in the mother’s womb. This causes more unconjugated bilirubin in the intestine to be easily reabsorbed into the bloodstream and to the liver.
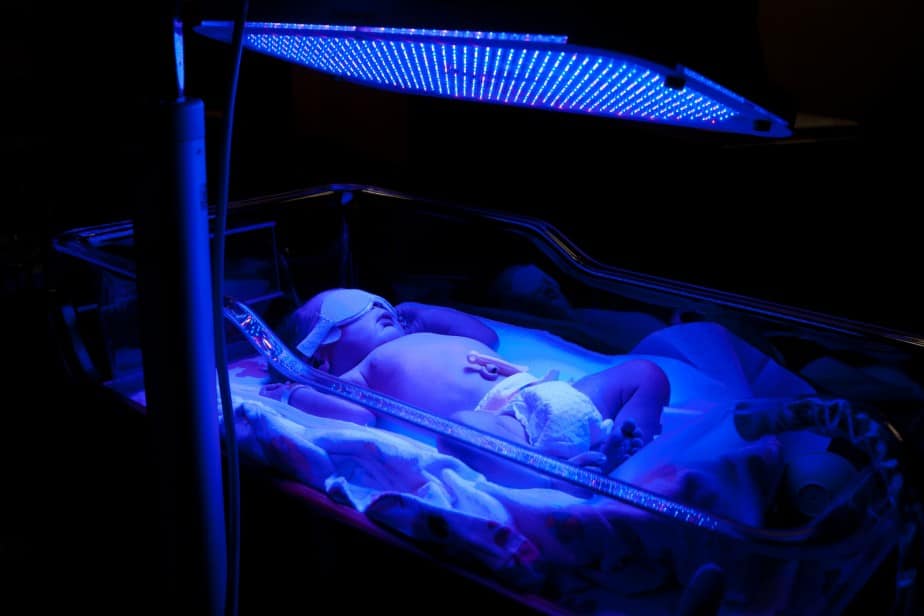
Treatment: Phototherapy
Most babies with jaundice don’t usually need treatment and the condition will get better within 10-14 days. Phototherapy is a treatment with a special type of light to lower the level of bilirubin in the blood through a process called photo-oxidation. This causes the bilirubin to be more water-soluble, so that they can be easily excreted.
Images

Keywords
-
Benign: Benign in medical, refers to a condition, tumour, or growth that is not cancerous.
-
Conjunctiva: The conjunctiva is a mucous membrane that covers the surface of the eyeball and posterior aspect of the eyelid that functions to protect the eye and allow the eyelids to move smoothly over the eye ball.
-
Sclera: The sclera, or white of the eye, is a protective covering that wraps over most of the eyeball. It extends from the cornea in the front to the optic nerve in the back.
-
Haemoglobin: Haemoglobin (Hb) is a protein found in the red blood cells that carries oxygen in your body and gives blood its red colour. Haemoglobin levels vary from person to person. Men usually have higher levels than women.
-
Glucuronosyltransferase: Glucuronyl transferase is a liver enzyme. It changes bilirubin into a form that can be removed from the body through the bile. It also changes some hormones, medicines, and toxins into non-harmful products.
-
Placenta: The placenta is an organ that develops in your uterus during pregnancy. This structure provides oxygen and nutrients to your growing baby and removes waste products from your baby’s blood.
-
Photo-Oxidation: Oxidation caused by the action of light. Photo-oxidation adds oxygen to the bilirubin so it dissolves easily in water.
References
Part 1
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/conjunctiva
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22088-sclera
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK310577/
Part 2
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002370.htm
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/placenta/art-20044425
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/jaundice-newborn/treatment/