Light

Fastest thing in the universe..?
Have you ever wondered what inspired Albert Einstein to come up with one of the greatest scientific theory? In this series you will learn the basic theory of special relativity and all of its fundamental element: light.
Part 1: The Speed of Light
Have you ever wondered what is the fastest thing possible in the universe? What is the so-called “maximum speed” something can ever travel at?
Sure, we all know that light, is travelling the fastest in the universe, having a speed of 299792458 m/s. Not infinite, but great enough to be fastest thing possible.. or is it? Let me show you an example:
Imagine you are walking in a moving train (same direction). Suppose your walking speed is V m/s and the speed of train is W m/s. So what is your speed? This question is ambiguous, because speed is relative. Relative to other stationary people on the train, your speed is just your walking speed, V. But relative to stationary people outside the train, your “total” speed is your walking speed V, + the speed of the train, W. (At least true logically).
Total speed = walking speed V + train speed, W.Notice anything weird? To C what i meant, we need to talk about the constant C: the speed of light. The speed of light is not only a constant, it is a constant in EVERY frame of reference. Using the previous example, if you are standing still in a moving train with speed W, and you shine a light the same direction as the moving train. Relative to any stationary object outside the train, the light will still be travelling at C, not C + W!
Yes, you can move as fast or slow or in whatever direction you want, and you will still always find light, travelling at C. Constant light speed is one of the 2 postulates of Albert Einstein’s special relativity (which will be covered in later chapter), and it will solve the seemingly paradoxical examples I’ve shown just now.
Images

Part 2: Time Dilation
Is time travel real..?
Have you ever wondered when can we achieve time travelling like what we’ve seen in those movies? Is time travelling into the future or into the past even possible?
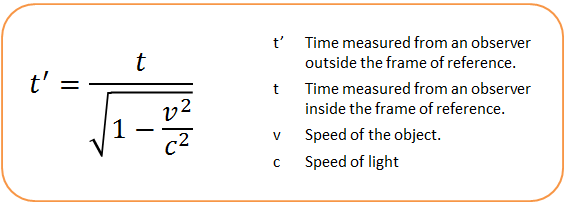
Well, it can be. In Albert Einstein’s special relativity, a clock that is moving relative to object in an inertial frame of reference (not accelerating) is measured to tick slower than a clock that is not moving. In other words, moving things’ time run slower than a stationary ones. As the famous quote goes the faster you move through space, the slower you move through time. It’s not obvious to us because the change is not noticeable at the speeds we usually travel at.
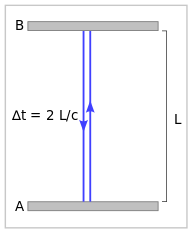
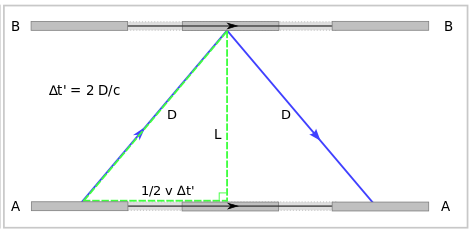
Time taken = distance/speedLooking at the example in the 2nd and 3rd pictures. Consider 2 mirrors A and B and a light pulse bouncing off them. If the 2 mirrors are stationary, we know that the time taken is the distance travelled 2L by the light pulse divided by the speed of light, C. Now if the 2 mirrors are moving at a constant speed, the light pulse is now taking a longer distance 2D. If we can agree that speed of light is always constant, then the time taken will be longer. At the stationary mirrors’ perspective, doing exactly the same thing, the moving ones tend to use a longer time, which only means that time is dilated, or is running slower when you are moving.
When you are moving near the speed of light, the change becomes more and more dramatic. Imagine this: if you are travelling at 99.94% the speed of light away from earth for 5 years, then take another 5 years to come back to earth. By that time, 29 years would’ve passed on earth, while you have only aged 10 years! Can I say that you have “time travelled” into the future?
So what happened when you travel at exactly the speed of light? Think about it!
Images

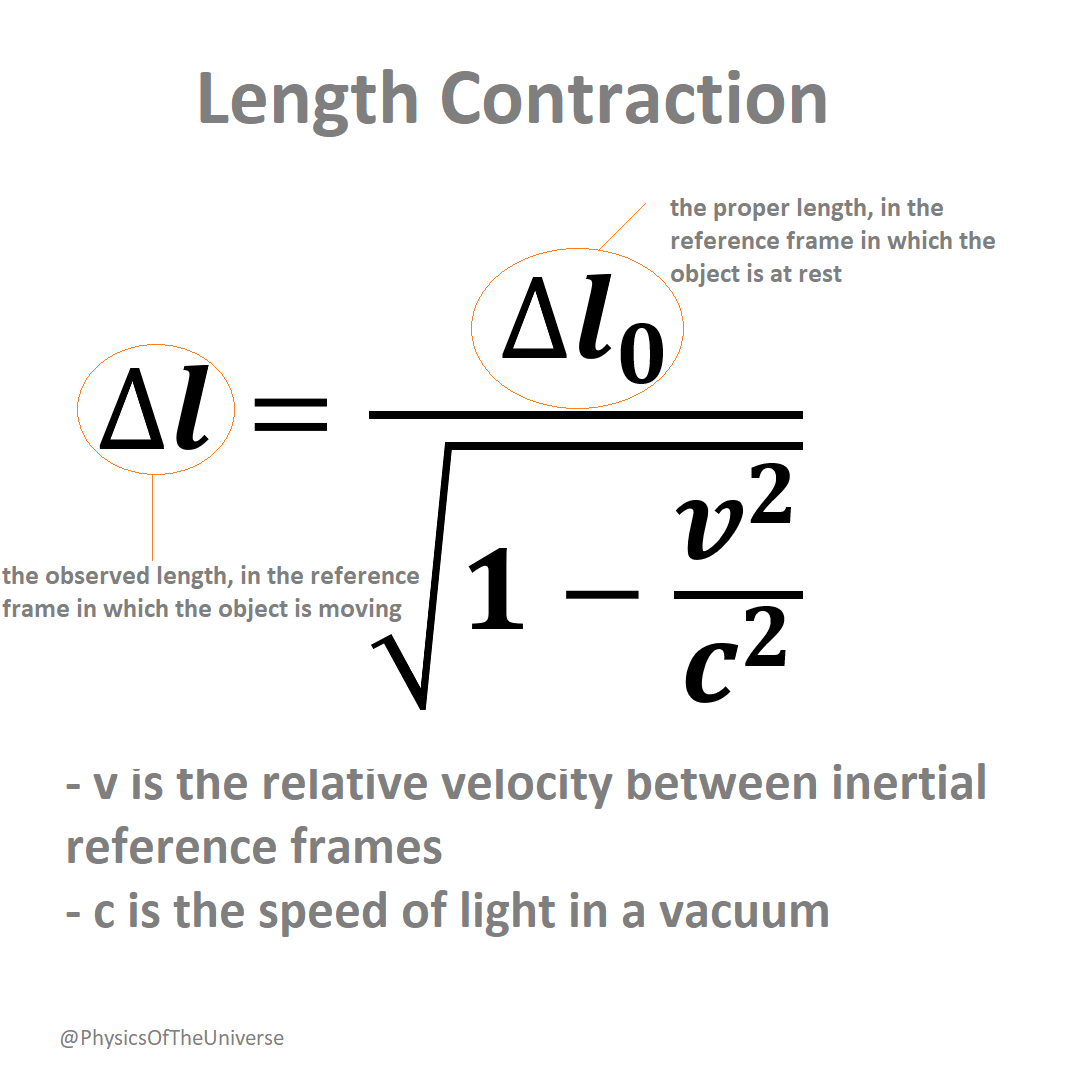
Part 3: Length Contraction
Moving makes you look shorter..
Have you ever wondered if a length or size of an object can change according to its speed or the observer’s speed? Sounds ridiculous right? Apparently moving not only affects your time, it also affects your sight. As it turns out, length is also relative. How?
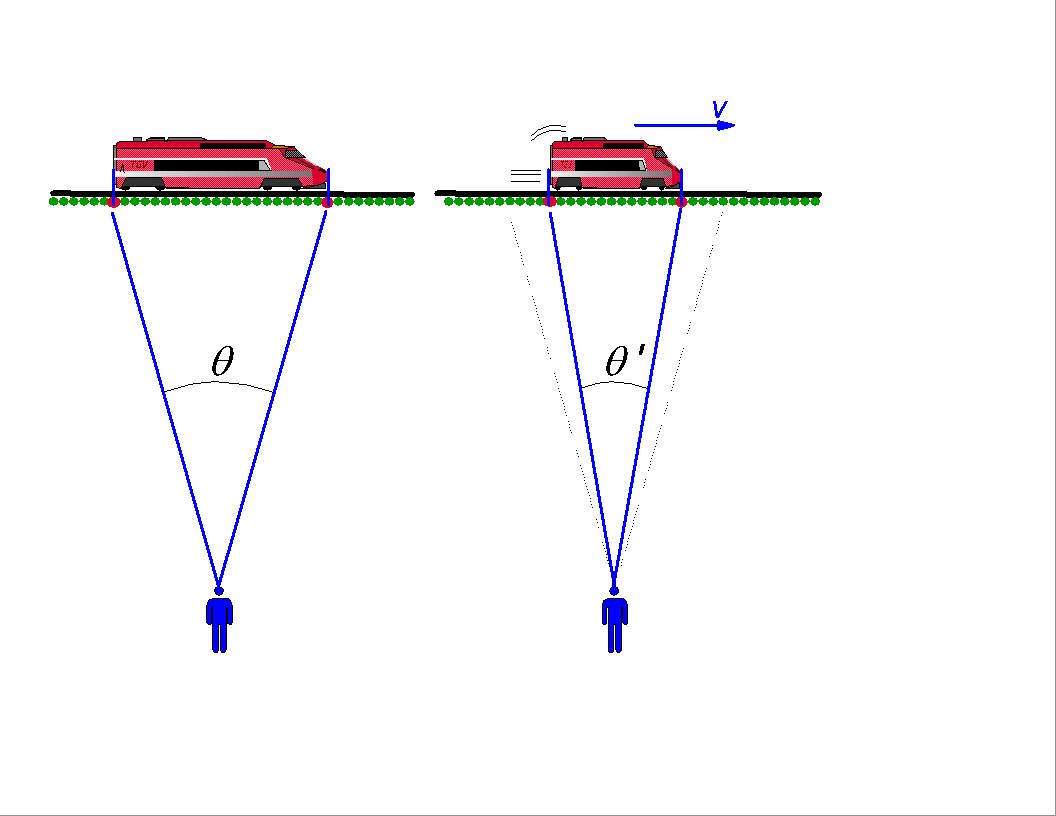
Similar concept to time dilation, for an observer in an inertial frame of reference, a moving object’s length appeared to be contracted and smaller. In other words, when you are moving relative to a stationary observer, the observer will perceive that your length being contracted, but for you, this change happens on the observer.
It is hard to measure a length of an object while the object is moving or while you are moving. The front and back of the object must be measured at the same time to your perspective. You can think of it as a snapshot of a moving object. The factor at which lengths are contracted again depends on how fast we’re moving relative to each other. And the closer we’re moving to light speed, the more relative perception of length become distorted.
To sum up both time dilation and length contraction, when you are moving at light speed, your time will be stopped, and the space around you will be contracted to a single point, which means that all 4 dimensions of spacetime no longer exists for you! Others will see you travelling forever before an instant even began for you.
Images
Part 4: Beyond light speed
Can we go faster?
Have you ever wondered in this vast universe, is there anything travel faster than the speed of light? In part 1 we discussed that nothing travels faster than the speed of light. So the “speed limit” in the universe is the speed of light.. right?
Maybe not. The 2 things that (might) travel faster than the speed of light: the expansion of the universe, and a hypothetical particle, tachyon. Put aside teleportation and quantum entanglement which does not involve any “travelling”.
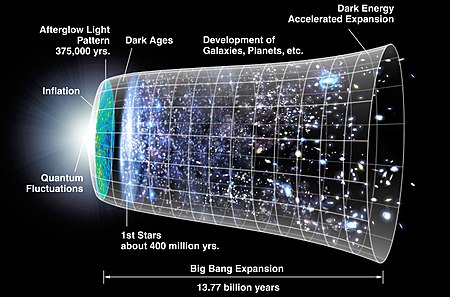
We know that after the big bang (born of the universe), the universe is expanding since then. But contrary to what we thought (expansion of universe should slow down due to gravity), the universe is expanding in an ever increasing speed. It is believed that the expansion of the universe has reached a speed beyond light, and we will never be able to see the edge of the universe because light coming from that is slower than its expansion!
A hypothetical particle tachyon always travels faster than light speed, but many physicists deny its existence because it violates the known law of physics. But if such particle does exist, time travel to the past will be possible because according to special relativity, the faster you move, the slower your time is. So beyond light speed, your time will be theoretically reversed. So what do you guys think? Is or will faster-than-light particle ever exist?
Images
Keywords
-
Albert Einstein: Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics.
-
Paradox: A paradox is a logically self-contradictory statement or a statement that runs contrary to one’s expectation. It is a statement that, despite apparently valid reasoning from true premises, leads to a seemingly self-contradictory or a logically unacceptable conclusion.
-
Inertial Frame of Reference: An inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference that is not undergoing acceleration. In an inertial frame of reference, a physical object with zero net force acting on it moves with a constant velocity (which might be zero).
-
Teleportation: Teleportation is the hypothetical transfer of matter or energy from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them. It is a common subject in science fiction literature and in other popular culture.
-
Quantum Entanglement: A phenomenon in which the quantum state of each particle of the group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, including when the particles are separated by a large distance. Measurements of physical properties such as position and spin performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated. For example, if a pair of entangled particles is generated such that their total spin is known to be zero, and one particle is found to have clockwise spin on a first axis, then the spin of the other particle, measured on the same axis, is found to be counterclockwise.
-
Big Bang: The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model explaining the existence of the universe from the earliest known periods. The model describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena.
References
Part 1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Albert_Einstein
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paradox
https://www.desy.de/user/projects/Physics/Relativity/SpeedOfLight/speed_of_light.html
Part 2
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inertial_frame_of_reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-O8lBIcHre0
Part 3
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-NN_m2yKAAk
https://www.cantorsparadise.com/length-contraction-in-einsteins-theory-of-relativity-7070ecd04e53
Part 4
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expansion_of_the_universe
https://www.britannica.com/science/tachyon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teleportation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_entanglement
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_Bang